How to Get Started with Laser Plastic Welding
Laser Plastic Welding Intro
Plastic part manufacturers increasingly turn to the power of laser plastic welding to assemble their parts. This cutting-edge technology offers several advantages, including fast, precise, clean welding that produces robust, airtight parts. It's no wonder that many professionals are eager to learn how to use this technique. This guide is designed to provide you with all the tools you need to take your plastic welding skills to the next level and revolutionize your manufacturing process.
The Basics
How does the laser welding process work? First, the two parts are clamped together with the IR transparent material on top and the absorbing material on the bottom. Next, the laser is transmitted through the top component and absorbed by the lower component, heating and melting the joint. Finally, the laser turns off, and the clamping force is maintained to allow the joint to cool and solidify. Put simply... clamp, heat, and cool.
Transmissive vs. Clear-to-clear
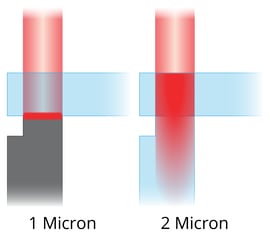
Laser welding uses two distinct wavelengths: the transmissive 1-micron wavelength and the clear-to-clear 2-micron wavelength. The transmissive wavelength operates by shining infrared energy through the transparent upper component and absorbing it into the lower component. The heat at the interface conducts outward, creating a heat-affected zone. It is important to have tight, intimate contact all along the weld joint to allow conduction.
The clear-to-clear wavelength, also known as 2-micron, is another prevalent type in laser welding. This wavelength partially absorbs and partially transmits through clear materials. Approximately 30% is absorbed in the upper component, another 30% in the lower component, and the remaining 40% gets lost. This distribution results in a larger heat-affected zone. Because transparent materials absorb this energy wavelength, there is no need for an opaque lower part, making it ideal for clear-to-clear applications.
Laser Welding Technologies
There are four main methods of applying the laser energy to parts.
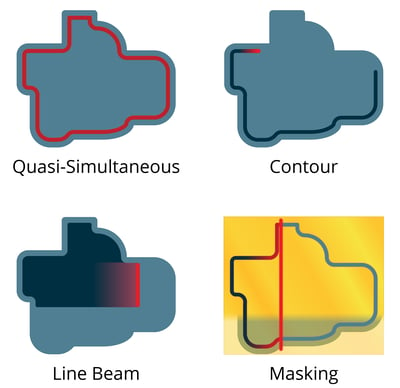
Quasi-Simultaneous
This method is cost-effective and the most utilized. It involves numerous quick passes along the weld path, quasi-simultaneously applying the laser energy to the whole weld joint. This approach is handy for T-style weld joints as it ensures consistent, simultaneous displacement within the joint.
Contour
Typically employed for large parts, contour laser welding uses a slower, single, continuous laser pass along the weld path. This method is suitable for flat-to-flat weld joints. However, contour welding has a challenge. The heat and displacement in the weld joint are uneven because the start point has cooled by the time energy is applied to the endpoint, adding stress to the weld.
Line Beam
Best suited for smaller parts, line beam laser welding spreads the laser energy into a curtain using optics. This curtain is then passed over the part like a wide paintbrush. This method is ideal for both small intricate parts and flat-area welding.
Masking
This method utilizes a precision-cut mask placed over the part to protect areas that do not require laser energy. Similar to the line beam method, masking also employs a laser curtain but offers higher precision, making it ideal for ultra-precise welding with weld ribs less than 0.7 mm wide.
Indicators You Need Laser Welding
Cleanliness
While no welding technology is flash-free, laser welding comes very close. And it does not produce any particulate. So you don't have to worry about contaminating your assembly.
Precision
The laser beam is accurate and precise, allowing you to weld miniature parts with small weld ribs. Of course, you can weld large parts as well. But in either case, you can expect precise results.
Fast
The laser beam can move very quickly, with intense energy. So, the weld joint heats up fast, resulting in short cycle times.
Read more about the benefits of laser plastic welding: Laser Plastic Welding is the Clean, Precise Process your Application Needs
Materials Compatible with Laser Welding
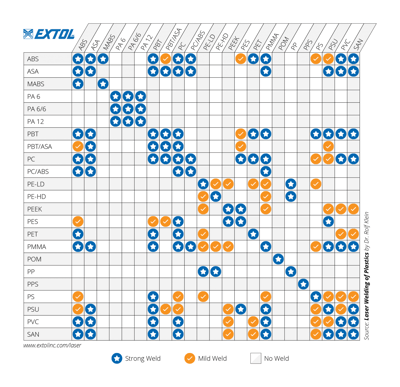
For laser welding to succeed, you need chemically compatible materials that bond. See our compatibility chart. At least one of the two components must be IR transmissive. There are even material colors that appear opaque but will transmit IR energy. If you can't make one of the components transmissive, you could consider Direct Laser Welding. Read more about that here. Lastly, fillers such as glass and talc can impact the laser welding process. Parts can still be welded in most cases, but fillers can slow down the process.
How to Customize Equipment around an Application
At Extol, we custom-configure every laser welding machine specifically for the application. This means you get a high-performing solution without overrunning your budget. We balance several essential factors to tailor the solution appropriately.
Cycle Time Requirements
How quickly do you need to produce welded parts? To reduce cycle time, we can increase the laser power. We can add automation features such as robotics, conveyors, and dials to handle the parts faster. We can even add multiple laser sources so more than one laser beam is welding the part at a time.
Budget
If you have a tight budget, we can look at ways to simplify the tooling. We can also lower the power of the machine. If your product volume is low enough, we may be able to offer contract manufacturing services.
Auxiliary Functions
Parts often need more than just laser welding. We commonly implement part marking, leak testing, vision inspection, short-shot detection, component installation, and much more. Extol can add these operations to the laser welder or integrate them into additional equipment.
Let Us Help You!
This article is just an overview of how to get started with laser plastic welding. To get connected with one of our laser welding experts, send us a note using the form below. We'll analyze your specific application and help you determine if it is suitable for laser plastic welding. We'll also help you design the best joint design. You can also check out our laser welding joint design guidelines to get started.
More Laser Plastic Welding Resources
Laser Plastic Welding Myths Debunked
Laser Plastic Welding is the Clean, Precise Process your Application Needs
The 4 Reliable Methods for Controlling & Predicting Laser Weld Quality